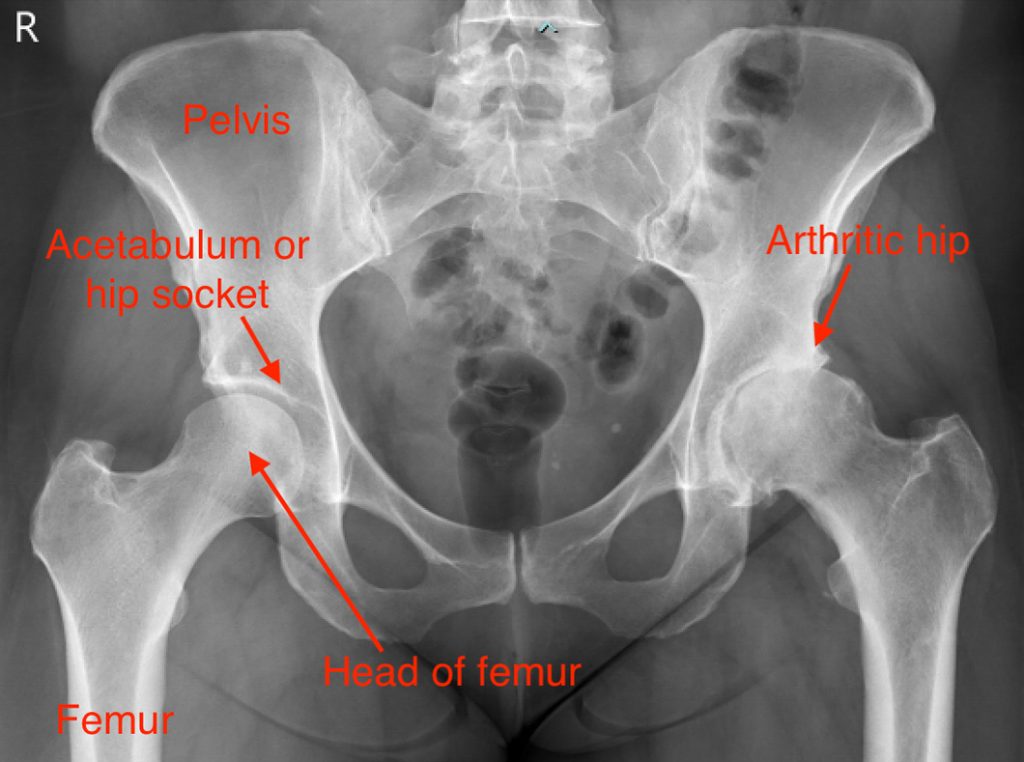
HIP ARTHRITIS TREATMENT
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENT
LOW COMPACT EXERCISE
It is vital to reduce activity initially until the pain resolves. Physical activity reduction may mean stopping running or other high impact activities. However, in the long term, walking, cycling, swimming and other water-based exercise is appropriate. If you continue to walk, avoid walking on hard surfaces such as concrete and wear walking shoes with good shock-absorbing qualities.
HEALTHY WEIGHT
If you are overweight, losing weight will reduce the load and stress on the knee. Weight loss can have a significant beneficial effect on the arthritis as well as improving your overall health.
MUSCLE STRENGTHENING
Loss of muscle mass starts in our thirties and worsens as we age. Arthritis will compound the problem. An appropriate exercise program, facilitated by a physiotherapist or an exercise physiologist, will strengthen your leg and improve its function. At a minimum should include the quadriceps, gluteal and “core” muscle groups.
INJECTIONS
Cortisone injections into the knee can be helpful for some people, mainly if there is an inflammatory component to the arthritis. The duration of benefit of a cortisone injection is variable. They also tend to be less effective with repeated injections.

MEDICATION
Medications may be required to help with the arthritic pain. Paracetamol is the recommended first-line analgesic. Paracetamol is useful for an acute flare of pain, or more regularly, as the arthritis worsens. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be helpful for short term use. Because of potential side effects, use caution for people with heart, kidney and gastrointestinal conditions. Therefore please discuss with your family doctor before using. COX-2 inhibitors such as Celebrex can be tried and are often better tolerated.
More potent analgesics such as opioid-containing drugs should be used cautiously and only for a short duration. Surprisingly they are often not that helpful for the pain of arthritis.
NON-PROVEN CURES
There are also many treatments purported to help or “cure” arthritis, but there is little evidence for their use. Glucosamine and chondroitin are two of the building blocks of cartilage. Although widely used, their benefit remains unproven. There is no scientific substantiation for many other heavily advertised supplements. Stem cell therapy is a costly and heavily promoted procedure with little evidence of its clinical benefit.
Arthritis or osteoarthritis is a condition where the articular cartilage of a joint is damaged and is progressively lost.
Call us on (03) 5223 3151 Book an appointment today.
SURGICAL TREATMENT
HIP REPLACEMENT
Hip replacement (or hip arthroplasty) has become the treatment of choice for people with end-stage arthritis. It is a significant procedure that involves removing the worn-out articular cartilage and then resurfacing the hip with metal and plastic components. Most people stay in the hospital for four to five days after the operation.
REHABILITATION
Rehabilitation to get the hip moving and to build up strength is critical to a good outcome. A rehab program should continue for a minimum of three months for you to obtain maximum benefit from the hip replacement. The vast majority of people get good pain relief and improved function.